4 minutes
Composition Over Inheritance - Strategy Pattern
Note : This article tries to summarize the major debate of “Composition vs Inheritance” from various articles/books. I tried to keep the examples/scenarios as concise & close to the original content as possible to make sure this sticks in your brain while studying the actual book.
Introduction
Knowing the OO Basics does not make you a good OO Designer. A good Object Oriented Designer makes sure the code is resusable, extensible and maintainable. Although Inheritance is a good knight in the shining armor, Like everything else in the Software Development, there are trade-offs to be made. Inheritance has its own flaws and is not meant as a solution for everything.
“Inheritance is surely a good answer but who knows the good questions. - Michel Gauthier”
- Favor Composition over Inheritance
“Composition over Inheritance in Object Oriented Programming is the principle that classes should achieve polymorphic behavior and code reuse by their composition (A class uses another object to provide some or all of its functionality) rather than an Inheritance from a base or parent class - Wikipedia”
Diving Deep…
Let say you work in a company that makes a simulator game, “WhatTheDuck”. In v1.0 of the game, you can see a large variety of ducks species swimming and making quacking sounds. Initial design of the game was built using basic OO techniques.
Now, We have a Duck superclass, from which all other duck types inherit.
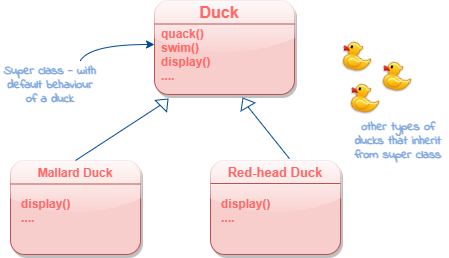
New Development Task : Implement a new feature that enables ducks to fly.
Solution-1
Add fly() method in Duck class and then all the ducks will inherit it.
Problem
Although this looks like a reasonable solution. As discussed earlier, A good OO designer thinks about reusability, Extensibility and Maintainability.
If we go with this idea, all ducks inherit the fly method and starts flying. What if we don’t want all types of Ducks to fly. Let’s say there is another type of duck (rubber duck) that should not fly. Its natural to use inheritance, but the disadvantages are,
- Code is duplicated across subclasses.
- Runtime behavior changes are difficult.
- Hard to gain knowledge of all Duck Behaviors.
- Changes can unintentionally affect other ducks.
Solution-2
Let’s think if Interface can be used. We could take the fly out method from super class and make a Flyable() interface with a fly() method. Now, only the ducks that are supposed to fly will implement that interface and have a fly method. Similarly, a Quackable() interface too.
Problem
This destroys the code reuse, duplicate code. What if there are more than one kind of flying behavior among ducks that do fly. Whenever there is a modification in code, We have to track all the subclasses of Duck and modify it. We are losing code reusability, Extensibility and Maintainability.
No matter how well you design an application, over time an application must grow and change or it will die.
Solution-3
Identify the aspects of your application that vary and separate them from what stays the same.
Here’s another way to think about this principle: take the parts that vary and encapsulate them, so that later you can alter or extend the parts that vary without affecting those that don’t.
We can see fly and quack behaviors are the ones creating problems. To separate these behaviors, lets pull both fly and quack methods out of Duck class and create new set of classes to represent each behavior.
Design-Pricinple : Program to an Interface and Not Implementation.
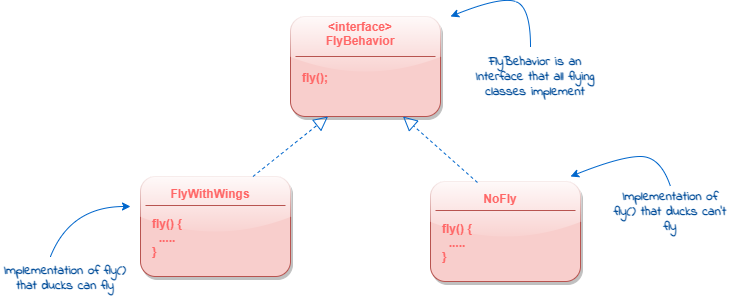
With this design, other types of objects can reuse our fly and quack behaviors since these are no longer in Duck class. Also, we can add new behaviors in future without modifying our existing behaviour classes or Duck super class. Therefore, We get the benefit of REUSE, without all the baggage that comes with Inheritance.
Creating Systems using Composition gives a lot of flexibility because It also allows us to change the behaviour at run time.
We have just applied a Design Pattern called — Strategy Pattern.
The Strategy Pattern defines a family of algorithms, encapsulates each one, and makes them interchangeable. Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from client that use it.
References : Wikipedia, Design Patterns - GoF, Head First Design Patterns (The Best), Checkout my github repo ‘Design Patterns’ for Source code